What Are Pre Packaged And Processed Foods?
July 20, 2022

You hear it all the time “I don’t have time” or even if you haven’t said it, surely you have experienced this phrase “instant gratification” having that urge to offer pleasure to the palate without any delay which has given rise to the so called “Convenience food” in the form of Pre-packaged or Processed foods. On the other hand, we also hear health experts advising to cut off Processed foods to prevent health issues. Should you simply avoid eating them? But what exactly are Pre Packaged and Processed foods? Is it as bad to consume as it sounds?
What exactly are Processed Foods?
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), processed foods are defined as any raw agricultural commodity that have been subject to washing, cleaning, milling, cutting, chopping, heating, pasteurizing, blanching, cooking, canning, freezing, drying, dehydrating, fermenting, mixing, packaging or other procedures that alter the food from its natural state.
For example, milk undergoes pasteurisation which is a method in which heat is used to eliminate potential harmful pathogens and extend shelf life. Here, the processing of milk may not necessarily involve additives or preservatives to maintain shelf life.
Fortification is another way of processing food to ensure dietary requirements of essential vitamins and minerals are met and fight nutrient deficiencies. For example, Milk is fortified with Vitamin D, Salt is fortified with Iodine and flours are enriched with vitamins and minerals.
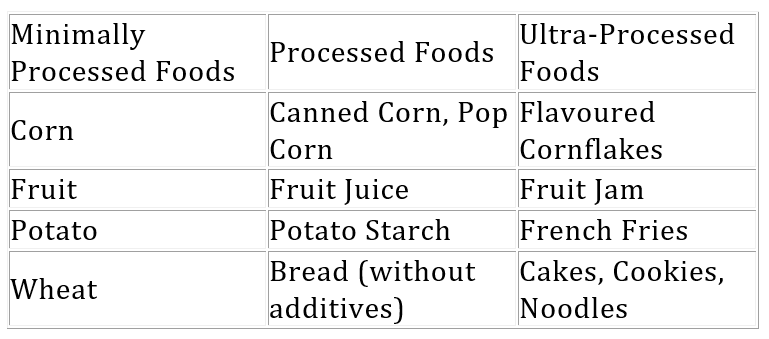
Food Classification According to Processing
The Nova System classifies food into four groups based on the degree of food processing.
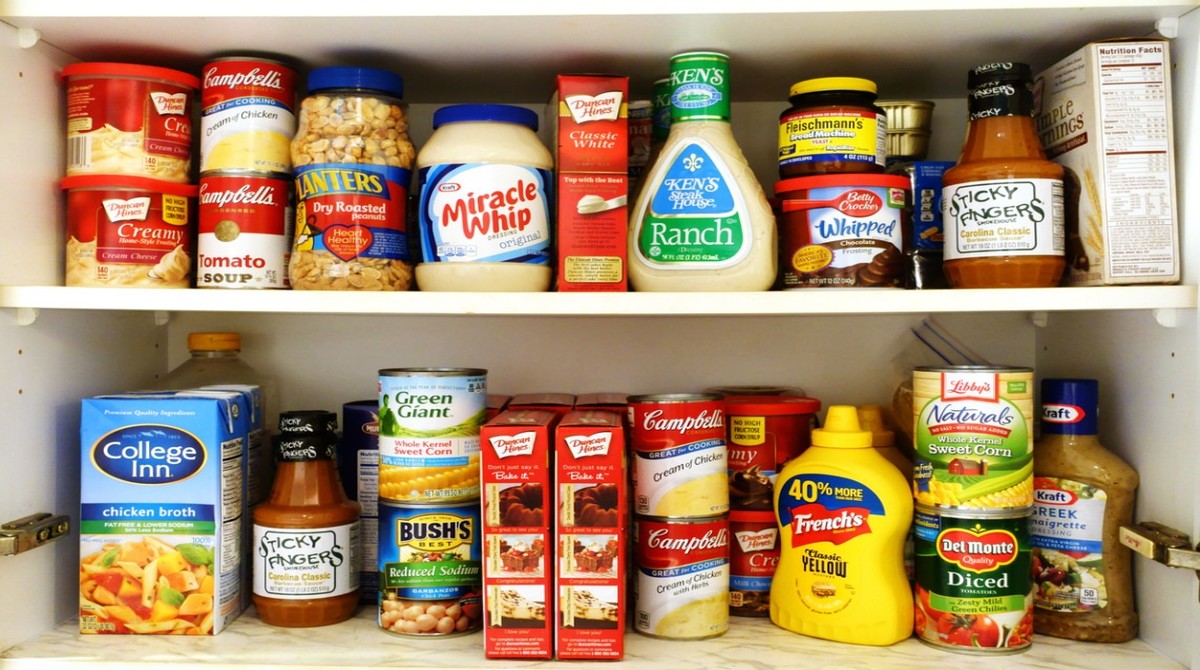
Unprocessed or Minimally processed foods- Food that are minimally altered from its natural form for the purpose of consumption and preservation without affecting the nutrient content of the food are known as minimally processed foods. For example, removing inedible or unwanted parts of the food, refrigeration, freezing and drying or other processes which do not add substances to the original food. Natural chilled or frozen fruits and vegetables, frozen meat, eggs, pasteurized milk, nuts, rice, and packaged cereal grains and flour without the addition of salt, sugar or other additives fall in this category.
Processed Culinary Ingredients- These food products are extracted from natural foods or from nature itself and cannot be consumed alone. These are ingredients used to cook meals. Examples include plant oil, butter, sugar, honey, and salt.
Processed foods- Processed foods are obtained by adding salt, sugar and other ingredients used to enhance the taste and appearance and shelf life of minimally processed foods. These are relatively simple products made without the use of additives. Examples include cheese, bread, canned vegetables and fruits, canned fish, salted nuts and seeds etc.
Ultra-processed foods- Ultra-processed foods are also known as highly processed foods. It undergoes several stages of processing, and has a higher amount of fat, salt, sugar, preservatives and other additives to ensure higher shelf life, and preserve the texture, flavour and palatability of food. Examples include ready to eat foods, instant noodles, prepared frozen meals, sauces, sugary flavoured beverages, confectionery, ice-creams etc.
What Are Pre-Packaged Foods?
According to FSSAI Food standards, Pre-Packaged food means “Food which is placed in a package of any nature, in such a manner that the contents cannot be changed without tampering with it and which is ready for sale to the consumer”.
It is self-evident by the word Pre-Packaged in terms of food which means, food packaged in a container before it is opted for sale or purchased by an individual. But food products which are offered for sale without packaging and then packaged by a vendor upon consumer request are not considered as Pre-packaged foods. All pre-packaged foods are considered to be processed foods. For example –
Meats and Chicken which are displayed on the counter that is sliced and packaged on request by the consumer cannot be termed as pre-packaged food.
On the other hand, frozen pre-chopped Chicken and Meat, Patties, Ham sealed in labelled containers at the grocery stores and supermarkets are considered as Pre-packaged food.
Also Read - What Are The Key Requirements For Declaration Of Ingredient Lists?
Some other examples of Pre-Packaged foods include
Assorted pre-peeled and cut fruits and vegetables.
Assorted Salad mix and Micro-Greens.
Frozen assorted chicken and meat.
Frozen fruits and vegetables trays.
Unsalted Almonds, Walnuts, seeds and others nuts
Assorted pre prepared food (Microwavable food)
Eggs packaged in boxes.
Cooked, sprouted beans, lentils etc.
Assorted Fish
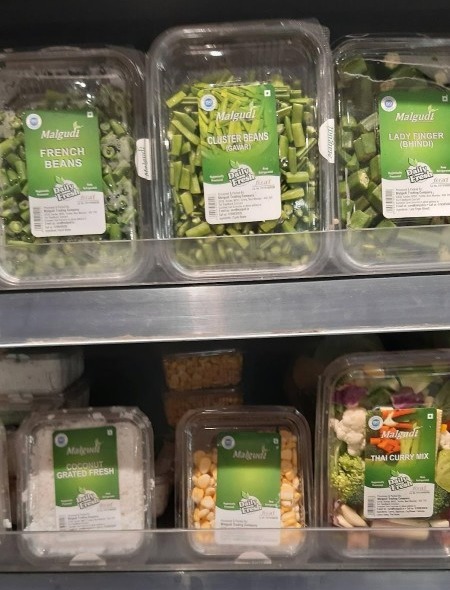

Pre-packaged food products

Pre-packaged Assorted Meal Prep
Are processed foods healthy?
Processed foods are often thought to be inferior to whole foods and considered to be a contributor of non-communicable diseases such as obesity, Type II Diabetes, Hypertension, Heart disease, etc. Virtually every food found in super markets would be considered processed to some degree because food undergoes deterioration from the time it is harvested. So when you think about processed foods it would be wise enough to ask how processed it is. Hence the focus should be on the consumption of minimally processed foods rather than ultra-processed foods.
There are many processed foods which are part of modern diet, some can be unhealthy due to the addition of high amounts of salt, sugar or fats and also due to the degree of processing. Consumption of such foods leads to eating more than the recommended amount of salt, sugar and fats. Hence the more food is processed the lesser the nutrient value of the product and the higher the risk of getting associated chronic diseases.
Examples of common highly processed foods include
Breakfast cereals
Baked food items- Bread, cakes, cookies
Health Drinks and Soft drinks
Savoury snacks
Ready to eat foods and microwave foods - Soups, pizzas, crisps, sausages
Processed Cheese, Flavoured Yoghurt, Flavoured Milk.
It is always better to know how processed the food is and be aware of your choices. Hence more emphasis should be given to reading Nutrition Information tables and Ingredient list which serves as an important tool to limit the amount of ultra-processed foods, emphasizing more on minimally processed foods rather than ultra-processed foods in the diet.

Minimally Processed Food Product

Processed Food Product

Ultra-Processed Food Product
Also Read - What Foods Are Required To Have A Nutrition Label?
References
Chapter 3. Food Standards.
Information on pre-packaged foods.
Companies need to print 'Best before' on pre-packaged food: Government. Aug 01, 2017,
Reasons parents buy pre-packaged, processed meals: It is more complicated than “I don’t have time”. Horning et, al. Journal of Nutrition education and Behaviour .January 2017
The Many Health Risks of Processed Foods The Many Health Risks of Processed Foods. Labourer’s Health and Safety Fund of North America. May, 2019; Vol 15, Number 12.
Ultra – Processed food’s impact on health. FAO- Document N-34
Processed foods and health.
Eating Processed foods.
What are Ultra-Processed food and are they bad for your health. Harvard health publishing blog. 09 January ,2020.

Olivia Crasto (MSc in Food Processing & Preservation)
Olivia is a Learner for Life, Eco enthusiast and loves to experience nature and its beauty
